Git repository: Link
Mathologer video:
Invidious
Youtube
On August 27, 2022, a youtube mathematician called the Mathologer published an interesting video on the mathematical constructs known as number walls. In the description of that video he also published a coding challenge of creating an implementation of the number wall algorithm.
This is not an entry into that coding challenge. This is just a tribute.
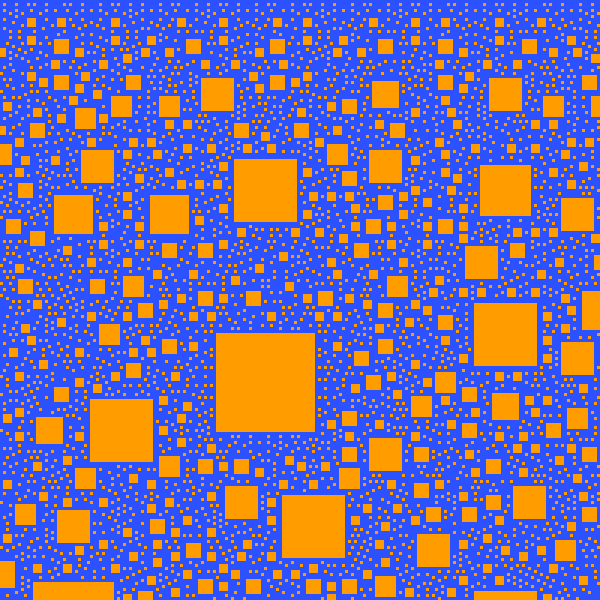
For various reasons this didn't end up finished in the time period required, and in any case it is not an online implementation and so doesn't qualify. But this project still has some fun tools to play around with for anyone with an interest in math. Amongst other things, elaborate pictures of the fractal square patterns produced by large number walls can be made.

It is strongly recommended that you watch the Mathologer's video for an explanation of what exactly a number wall is. If, for some reason, you don't want to do that or the video is inaccessible, then the rules of how to construct a number wall are detailed in the appendix.
There are three programs provided:
An example of using wallsolve to calculate the next number in the sequence of integer cubes:
> wallsolve -i 1,8,27,64,125,216,343,512,729,1000 S(n) = 4S(n-1) - 6S(n-2) + 4S(n-3) - S(n-4) Next: 1331 >
An example of visualwall has already been given in the overview in the form of the picture of the Pagoda sequence number wall, and the output of wallgen is too verbose to show here.
All calculations to produce the number walls in these programs are done using the simple construction rules in the appendix. No determinants were used, as that method would be more computationally intensive.
Since the methods of constructing a number wall given by the Mathologer assume a sequence that is infinite in both directions and any sequence used by these programs is finite, some compromises had to be made. In particular, visualwall uses a longer sequence to generate its number wall and then fits the largest square viewing area it can inside the resulting triangle of calculated values.
The polynomial library made for wallsolve assumes that coefficients will always be integers. This applies even to the division implementation, with only integer division being used and the remainder term becoming larger than it may otherwise be expected to be if rationals were permitted. As a number wall calculated from an integer sequence (or a sequence of polynomials with integer coefficients) will always have integer values, this isn't actually a problem. But care had to be taken in number wall construction so that division operations were always left until last.
The modulus values allowed by visualwall are not limited to prime numbers. If a composite modulus is selected then the highlighted portions of cells equal to zero modulo that number may not produce squares. The resulting pictures are, however, still interesting to examine.
At present visualwall only has the option to display either the Pagoda sequence or a sequence of random numbers, unless a comma separated value formatted sequence is supplied in an external file. It would not be hard for anyone with a passing knowledge of OCaml to add in different sequences, but at this stage there is no need.
A number wall is a grid of numbers that extends infinitely left, right, and down. It begins with an infinite row of ones at the top, then below that a row containing the input sequence. All other cells are computed according to the following rules.
| Pattern | Relation | Notes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
or alternatively where |
This rule is used to calculate the vast majority of cells. |
| Pattern | Relation | Notes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
or alternatively where |
If cell goes out of bounds of the wall, it is considered equal to zero. |
| Pattern | Relation | Notes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
where
is the common ratio of the arithmetic sequence is the common ratio of the arithmetic sequence is the common ratio of the arithmetic sequence is the common ratio of the arithmetic sequence is equal to if the dimension of the zero square is even, or if the dimension is odd |
All cells surrounding a square of zeros are guaranteed to be nonzero. This rule is applicable to squares of zeros of any finite size, but for the sake of simplicity the previous rule should be used for isolated zeros. The cells that this rule should be targeted at calculating are those on the bottom row below the square of zeros. Reformulating the math to solve for those cells is left as an exercise to the reader. |
| Pattern | Relation | Notes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
where are the common ratios of the arithmetic sequences along the sides of the square of zeros as in the Horseshoe Rule is equal to if is odd and if is even |
As with the Horseshoe Rule, this rule is applicable to squares of zeros of any finite
size. The cells that this rule should be targeted at are those along the bottom denoted as but as with the previous rule, reformulating the math to solve for those cells is left as an exercise to the reader. As with the Long Cross Rule, if any of the cells go out of bounds of the wall they are considered to be equal to zero. This can occur if there are non-isolated zeros in the input sequence. |
An example of a number wall:
| ⋯ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ⋯ |
| ⋯ | 64 | 125 | 216 | 343 | 512 | 729 | 1000 | ⋯ |
| ⋯ | 721 | 1801 | 3781 | 7057 | 12097 | 19441 | 29701 | ⋯ |
| ⋯ | 2016 | 4140 | 7344 | 11844 | 17856 | 25596 | 35280 | ⋯ |
| ⋯ | 1296 | 1296 | 1296 | 1296 | 1296 | 1296 | 1296 | ⋯ |
| ⋯ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ⋯ |
| ⋰ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋱ |
The above excerpt was taken from the number wall generated by the sequence of integer cubes. In this case, the wall essentially ends in a row of all zeros as all subsequent rows below that will also be zeros. Note however that this does not always happen.
A property of number walls is that zeros will always be arranged in squares. A singular isolated zero is considered to be a 1x1 square and a wall ending in rows of zeros as above is considered to be the start of a square of zeros of infinite size. This property can be used to supplement the calculation rules.
{% endblock -%}